Art Appreciation
Understanding Art History, Artists & Culture
What is Art Appreciation?
What We Teach In Our Class Room
Art appreciation is a critical and mindful engagement with works of art. It involves examining and evaluating various forms of art, such as painting, sculpture, architecture, photography, and more, in order to gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of their cultural, historical, and aesthetic significance.
By learning to appreciate art, we not only gain a greater understanding of the world around us, but we also develop a keener eye for beauty and a more nuanced understanding of the human experience. Whether you are an experienced art enthusiast or just starting your journey, this page is dedicated to helping you deepen your appreciation of art.
Art Lessons Contains
Visual Elements of Art

Line
Freehand lines, Mechanical lines, Continuous lines, Broken lines, Thick lines, Thin lines
Element of Art Line
Line is the foundation of all drawing. It is the first and most versatile of the visual elements in art.

Shapes
Shapes can be employed in art to alter your feelings about a piece’s tone and composition.
Element of Art Shapes
2D and 3D Shapes, Representational Shapes, Abstract Shapes, Positive & Negative shapes, Geometric Shapes, Symbolic & Decorative, Perspective shapes, Transparent, Reflective and Opaque Shapes
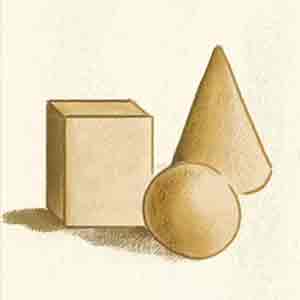
Forms
Form is the main visual element in sculpture, 3D design and architecture.
Element of Art Forms
2D and 3D forms, Forms as Carving, Wood Carving, Form as Modelling and Casting, Form as Light and Space, Form as Land Art, Form as Kinetic Art
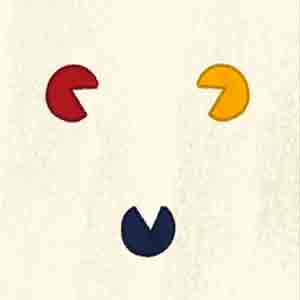
Space
In a work of art, space refers to a sense of depth or three dimensions.
Element of Art Space
Positive space (the area of the work filled by the topic or subjects), negative space (the region around the subject or subjects), and three-dimensional space

Texture
Surface quality of an artwork – the roughness or smoothness of the material used to create.
Element of Art Texture
We experience texture in two ways: optically (through sight) and physically (through touch).

Value
Value or Tone is the degree of lightness or darkness of a color.
Element of Art Value
Tone As the Contrast of Light and Dark, Tone as Form, Tone As Drama, Tone as Tranquility, Tone as Depth and Distance
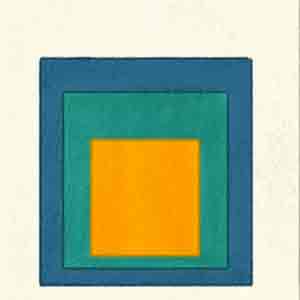
Colors
Visual element with greatest emotional impact. Creates mood or atmosphere.
Element of Art Colors
Color as light, tone, pattern, form, symbol, movement, harmony, contrast, mood
Tools you will be using a lot
Visual Principles of Art

Patterns
Principle of Art- Pattern
A regular arrangement of alternated or repeated elements (Shapes, Line, colors) or motifs

Contrast
Principle of Art- Contrast
The Juxtaposition of different elements of Design (for e.g. rough and smooth texture, dark and light values)in order to highlight their differences and / or create visual interest or a focal point.

Emphasis
Principle of Art- Emphasis
Special attention/importance given to one part of a work of art (Eg aa dark shape in light composition) Emphasis can be achieved through placement, contrast, color, size, repetition.. released to focal point.

Balance
Principle of Art- Balance
A Feeling of balance results when the elements of design are arranged symmetrically or asymmetrically to create the impression of equality in weight or importance.

Scale
Principle of Art- Scale
The relationship between objects with respect to size, number, and so on, including the relation between parts of a whole.

Harmony
Principle of Art- Harmony
The arrangement of elements to give the viewer the feeling that all the parts of the piece form a coherent whole.

Rhythm / Movement
Principle of Art- Rhythm
The use of recurring elements to direct the eye through the image; the way the elements are organised to lead the eye to the focal area. The eye can be directed.

Unity
Principle of Art- Unity
All part of an image works together to be seen as whole.
Materials & Tools To create
Art Medium
Art medium refers to the material and tools an artist uses to create a work of art. It can include a wide range of materials such as paint, ink, charcoal, clay, wood, metal, textiles, and digital media. Each medium has unique properties and can be used to create different effects and styles in art.
The choice of art medium depends on the artist’s intentions, style, and the desired outcome of the artwork. For example, an artist may choose oil paint for its vibrant colors and blending ability, or charcoal for its smudgy and textured appearance. They may also experiment with different media to create mixed media art, which combines multiple mediums and techniques to create a unique and complex work of art.

Pencil

CHARCOAL

Acrylic & oil

oil & Soft pastels

watercolor

Craft

Clay

Paper Mache

Stop Motion

GIMP

Lino

wire

Print Media

Digital Publishing

Photo Manipulation
Importance of Art movements
Modern Art Movements

Impressionism
Impressionism was a late 19th century art movement in France. The Impressionists are famous for their vibrant painting styles and use of color.

Post-Impressionism
Post-impressionism was the name given to numerous painting styles that emerged at the close of the nineteenth century. It was not a formal movement or style.
Cubism
The earliest abstract art style was Cubism. Cubist painting abandoned the tradition of perspective drawing in favor of displaying several viewpoints of a subject at once.

Fauvism
Fauvism is a vivid painting style pioneered by Henri Matisse and André Derain, who used vibrant colors, simplified drawing, and expressive brushwork.

Expressionism
Expressionism is an early 20th century type of art that is infused with an emotional or spiritual vision. It is a German-based artistic movement.

Dadaism
Dadaism, often known as Dada, was a type of artistic anarchy that questioned the social, political, and cultural ideals of the day.

Surrealism
Surrealism is a twentieth-century art movement that investigated the hidden depths of the unconscious mind.

Pop Art
Pop Art was a 1960s modern art movement that incorporated imagery from mass media, mass production, and mass society.

Op Art
Op Art Short for Optical Art, is a style of visual art that uses Optical illusions. Artists use shapes, colours and patterns create images that look they are moving or blurring.
Major Artist, styles and key paintings
Art History Timelines
Our Art History Timelines provide a straightforward description of the major art movements, showcasing prominent artists and paintings from each movement. Understanding a movement or artist’s place in the timeline of art history is essential to appreciating their work completely. Knowing the creative and historical environment in which a piece of modern art was produced is instructive because most contemporary art is a reaction to or development of a prior style in the timeline.

Western Art History
Byzantine Art (330-1450), Gothic Art (1150-1400), Renaissance (1400-1450), Mannerism (1520-1580, Baroque (1600-1700), Rococo (1700-1775),Romanticism (1765-1850), Realism (1840-1880) | Impressionism (1870-1890), Post Impressionism (1885-1905), Fauvism (1905-1910, Cubism (1907-1915), Futurism (1909-1914), Abstract Art (1907-), Dada (1916-1922), Surrealism (1924-1939), Pop Art (1954-1970), Op Art (1964-1970)

Indian Art History
The Rajasthani School Of Painting, The Pahari School Of Painting, The Mughal Painting, The Bengal School of Paintings, Modern trends in Indian Art – Jamini Roy, Amrita Sher Gil, M.F Husain

Art & Culture Around the world
Warli, Bhil, Gond Art, Madhubani Painting, Saura Art, Miniature Painting, Kalihat Paintings, Amate Bark, Huichol, Mola Art (Central America)… And more
Artist Introduction
Artists

Victor Vasarely
Op Artist

Bridget Riley
Painter / Op Artist

Hokusai
Japanese artist / Printmaker

Georgia O Keeffe
Modernist Artist

Ted Harrison
Canadian artist

Mary Blair
American artist

Jamini Roy
Indian Artist

Amrita Sher-Gil
Hungarian-Indian painter

Raja Ravi Varma
Indian Artist

Rabindranath Tagore
Indian Artist

Sayed Haider Raza
Indian artist

Nandalal Bose
Indian artist

Jan Brueghel the Elder
Renaissance painter

Claude Monet
Impressionist

Vincent Van Gogh
Post-Impressionist

Pablo Picasso
Cubism

Henri Matisse
Fauvism
