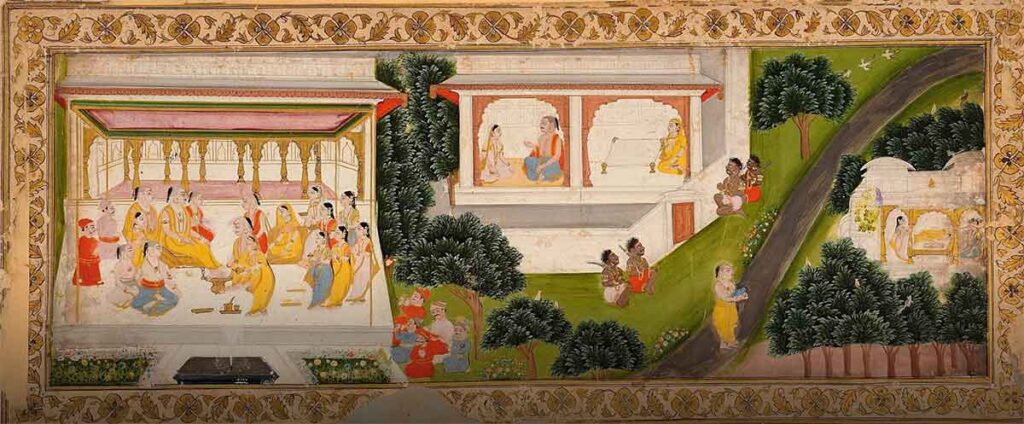
India is a country that is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, which is reflected in its art and architecture. One such form of art that has captured the imagination of art lovers worldwide is Pahari painting. Pahari painting is a style of Indian painting that originated in the hilly regions of northern India, particularly in the states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. This art form has been practiced in the region for centuries and continues to thrive to this day. In this blog, we will explore the history, techniques, and themes of Pahari painting, as well as its significance in Indian art.
History of Pahari Painting
Pahari painting has a long and fascinating history that dates back to the 17th century when the Mughal emperor Jahangir commissioned a group of painters to create artworks in the hilly regions of northern India. These painters, known as the Kulu artists, were renowned for their exquisite miniature paintings, which were characterized by their delicate brushwork, intricate details, and vivid colors. Over time, the Kulu artists developed their distinctive style of painting, which came to be known as Pahari painting.
Techniques of Pahari Painting
One of the unique features of Pahari painting is its technique, which involves the use of natural pigments and dyes to create delicate brushwork and vivid colors. The artists use a combination of brushwork and wash technique to create subtle shading and tonal variations, which gives the paintings a sense of depth and realism. The brushwork is executed with such precision that it results in intricate details, especially in the intricate borders and delicate facial features of the paintings.
The Pahari painting technique is characterized by the use of natural materials such as ground mineral pigments, gold and silver leaf, and vegetable dyes. The pigments are mixed with a binder made from gum arabic or gum tragacanth, which gives the paintings a translucent quality. The technique also involves the use of special brushes made from animal hair, which allows the artists to create fine lines and delicate details. The combination of these materials and techniques results in the vibrant and intricate Pahari paintings that are admired by art lovers all over the world.
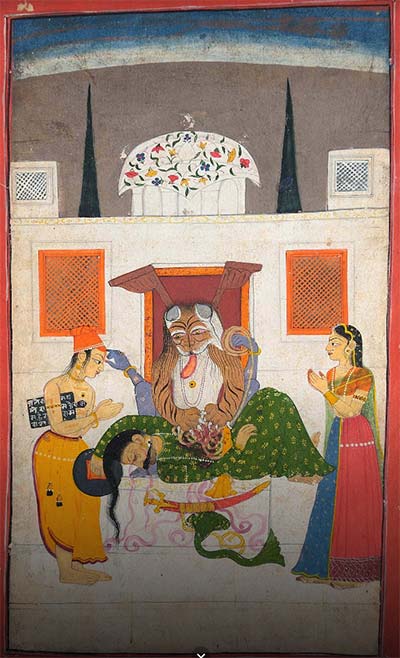



Types of Pahari Painting
The art form has evolved over time, and various styles and types of Pahari painting have emerged. Each type of Pahari painting has its unique characteristics, themes, and styles. In this blog, we will explore some of the most popular types of Pahari painting.
1. Basohli Painting: Basohli painting is one of the earliest styles of Pahari painting, which emerged in the late 17th century. The paintings are characterized by their vibrant colors, bold outlines, and expressive facial features. The themes of Basohli painting are primarily religious and depict scenes from Hindu mythology.
2. Kangra Painting: Kangra painting emerged in the 18th century and is characterized by its delicate brushwork and subtle colors. The themes of Kangra painting are predominantly romantic and depict scenes from the love life of the Hindu deity Krishna and his consort Radha. The paintings are known for their ethereal beauty and convey a sense of divine love and romance.
3. Guler Painting: Guler painting is another style of Pahari painting that emerged in the 18th century. The paintings are characterized by their delicate brushwork, intricate details, and subdued colors. The themes of Guler painting are primarily religious and depict scenes from the lives of Hindu deities, particularly Lord Krishna.
4. Chamba Painting: Chamba painting emerged in the 18th century and is known for its bold colors and expressive brushwork. The themes of Chamba painting are primarily religious and depict scenes from the lives of Hindu deities, particularly Lord Shiva. The paintings are characterized by their large, bold figures and dynamic compositions.
5. Mandi Painting: Mandi painting is a relatively lesser-known style of Pahari painting that emerged in the 18th century. The paintings are characterized by their bold outlines, vibrant colors, and intricate details. The themes of Mandi painting are primarily religious and depict scenes from the lives of Hindu deities, particularly Lord Vishnu.
Themes of Pahari Painting
This art form has a rich history and is renowned for its delicate brushwork, intricate details, and vivid colors. The themes of Pahari painting are often religious or mythological in nature, and the paintings typically depict scenes from the lives of Hindu deities such as Krishna, Radha, and Shiva. In this blog, we will explore the various themes of Pahari painting and their significance in Indian art and culture.
1. Religious Themes
Religious themes are a predominant feature of Pahari painting. The paintings often depict scenes from the lives of Hindu deities, and the artists use subtle gestures and facial expressions to convey the mood of the scene. For example, the paintings may depict Lord Krishna playing the flute, Radha and Krishna in a romantic embrace, or Lord Shiva meditating in the Himalayas. These paintings not only depict the religious beliefs of the people but also capture the essence of Indian mythology and spirituality.
2.Courtly Themes
Another common theme of Pahari painting is courtly themes. The paintings often depict the lives of royalty and aristocrats, such as kings, queens, and nobles. The artists use rich colors and intricate details to portray the opulence and grandeur of the royal courts. The paintings may depict courtly scenes such as the king on a hunting expedition, the queen playing a musical instrument, or the noble engaged in a game of chess.
3. Nature Themes
Nature themes are also prevalent in Pahari painting. The hilly regions of northern India are known for their natural beauty, and the artists often draw inspiration from the flora and fauna of the region. The paintings may depict scenes such as a peacock dancing in the rain, a bird perched on a tree branch, or a deer drinking from a stream. These paintings not only showcase the beauty of nature but also reflect the deep connection between humans and the natural world.
Significance of Pahari Painting
Pahari painting is a significant art form in Indian art and culture. It is renowned for its exquisite beauty, intricate details, and vivid colors, and it has influenced other forms of Indian painting such as Rajasthani and Kangra painting. Pahari painting has also played a vital role in preserving the rich cultural heritage of the hilly regions of northern India, and it continues to be an essential part of the region’s artistic and cultural identity.
1. Cultural Significance: Pahari painting is an integral part of Indian culture, and it reflects the deep connection between art and spirituality in India. The paintings depict scenes from the lives of Hindu deities and convey the rich mythology and spiritual traditions of India. Pahari painting is also a medium through which the cultural traditions and customs of the people of northern India are conveyed.
2. Artistic Significance: Pahari painting is renowned for its delicate brushwork, intricate details, and vivid colors. The artists use natural pigments and dyes to create the paintings, and they often use a combination of brushwork and wash technique to create subtle shading and tonal variations. The paintings are characterized by their intricate borders, elaborate costumes, and delicate facial features, which reflect the artistic excellence of the Pahari artists.
3. Economic Significance: Pahari painting is not only a cultural and artistic heritage but also an economic asset for the people of northern India. The paintings are sold in various art galleries and handicraft stores, and they provide employment opportunities for the local artisans and craftsmen. The sales of Pahari paintings also contribute to the tourism industry of the region, as tourists are attracted to the unique and beautiful art form.
4. Historical Significance: Pahari painting has a rich history that spans several centuries. The art form flourished during the 17th and 18th centuries under the patronage of the Rajput kings, who commissioned the artists to create paintings for their courts and palaces. The paintings also reflect the cultural exchanges that took place between northern India and the neighboring regions of Tibet and Nepal, as the artists were influenced by the art styles of these regions.
In conclusion, Pahari painting is a highly revered art form that has been practiced in the hilly regions of northern India for centuries. Its intricate details, vivid colors, and delicate portrayal of emotions have made it an important part of Indian art and culture. The art form continues to thrive to this day, and its significance in preserving the rich cultural heritage of the region cannot be overstated. Pahari painting is an excellent example of the beauty and diversity of Indian art, and it continues to inspire artists and art lovers worldwide.